The <icon> section in a <layer> controls the drawing of icons for point objects. Icons are specified using SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics). The <icon> attributes are:
- angle: a value in degrees clockwise from true north (for SVG icons only); if specified, the icon is drawn at that angle relative to the map, instead of the normal system of drawing the icon upright. You can also use the _angle attribute in a map object to get the same result.
- canCombine: if the value is "yes" or "true" multiple instances of this icon are combined (at the time of drawing the map) when too close together. By default icons do not combine. Combined icons are given the attribute _combined=N, where N is the number of original icons combined.
- canOverlap: if the value is "yes" or "true" the icon can overlap other icons. By default icons are not allowed to overlap. Non-overlapping icons are drawn only if they would not overlap other non-overlapping icons. Overlapping icons are always drawn.
- color: if present, overrides the natural color of the icon as defined by the SVG code; the icon is drawn in monochrome, colorising it using the specified color
- colorAttrib: the name of a map object attribute giving the color of the icon; the default map object attribute name is _color. Map objects having the specified attribute use it as the icon color.
- height: height of the icon; when the icon is rendered it is scaled to this height; if width is not set it is calculated automatically, preserving the aspect ratio of the SVG graphics
- hotSpotX: x coordinate of the icon's hot spot, which is the point on the icon to be positioned at the point of interest on the map; defaults to 50% of the icon's width; percentage values refer to the width of the icon
- hotSpotY: y coordinate of the icon's hot spot, which is the point on the icon to be positioned at the point of interest on the map; defaults to 50% of the icon's height; percentage values refer to the height of the icon
- id: the name by which an icon can be referenced elsewhere in the style sheet. Icons can be referenced anywhere after their definition, whether they are defined in a <defs> section or at their point of first use in a layer.
- labelX, labelY: x and y coordinates of the label position, relative to the hotspot, if a label is to be drawn on top of the icon (as in US Highway shields). The label is centered on this position. Percentage values refer to the width and height of the icon. The default values are both 0, meaning that the label is drawn over the hotspot. Percentage values refer to the height of the icon.
- priority: the label priority, with the same meaning as it has in <label>; this attribute allows you to set the label priority if a label consists of an icon only. This attribute works only if it is part of the <icon> element in a <layer>, not if it is specified in the <icon> element in the <defs> section.
- ref: a reference to an icon defined previously in the <defs> section of the style sheet. If a <ref> is present, the <svg> section is taken from the <icon> in the <defs> section.
- refAttrib: the name of a map object attribute containing the icon reference; if this is specified, for any map objects having the attribute, the value of the attribute is used to select the <icon> from the <defs> section
- text: the text for an icon made from a character or characters rather than SVG graphics
- textAttrib: if not empty, the name of a map object attribute giving the icon text, for use with icons consisting of one or more characters. Overrides text.
- width: width of the icon; when the icon is rendered it is scaled to this width; if height is not set it is calculated automatically, preserving the aspect ratio of the SVG graphics
Every <icon> section that does not load a predefined icon using the ref attribute must contain an <svg> section defining the icon using a subset of the Scalable Vector Graphics language. CartoType supports the following SVG graphic elements fully: <g>, <rect>, <circle>, <ellipse>, <line>, <polyline>, <polygon>, and <path>, and partially supports <text>.
Here is a sample <icon> section containing some SVG code to draw a large blue letter H to indicate a hospital:
<icon width='70m,16pt,100pt'> <svg width='80' height='100'> <g stroke='blue' stroke-width='20'> <line x1='10' y1='0' x2='10' y2='100'/> <line x1='70' y1='0' x2='70' y2='100'/> <line x1='10' y1='50' x2='70' y2='50'/> </g> </svg> </icon>
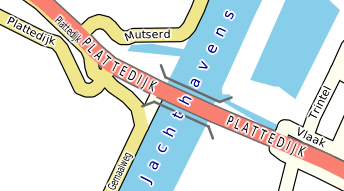
Graphics can be used to indicate bridges and ramps (roads connecting limited-access roads like motorways to other roads). They consist of an optional shadow under the bridge, and optional lines at the side of the bridge, with user-definable ends.
Bridge graphics are drawn for roads with the bridge attribute, and ramp graphics are drawn for those with the ramp attribute.
The bridge graphics above are drawn using this style:
<bridge width='45m,2pt' border='dimgrey' borderWidth='14%,1' endPath='l 512 512' maxScale='50000'/>
You use the <bridge> or <ramp> tag inside a < layer> tag (or inside a <condition> in a layer). The <bridge> and <ramp> attributes are:
- border: the border color
- shadow: the shadow color
- width: the width of the bridge (distance between bridge borders)
- borderWidth: the width of the border strokes
- shadowWidth: the width of the shadow
- shadowOffsetX: x offset of the shadow, relative to the road
- shadowOffsetY: y offset of the shadow, relative to the road
- maxScale: maximum scale (denominator) at which the bridge graphics are drawn
- endPath: a path, using SVG path syntax, for strokes appended to the ends of the bridge sides. It gives one of the four ends only: that of the top right end, if the bridge is drawn horizontally. The other ends are generated by transforming the path as needed. The path units are 1024ths of the line width unless modified by unitsPerLineWidth.
- unitsPerLineWidth: the size of the units in endPath, defined as the number of units equal to the line width. The default value is 1024
- fill: if present, the fill color for the bridge or ramp; if absent, the bridge or ramp inherits the road color.
- lineBorder: if present, the line border color for the bridge or ramp; if absent, the bridge or ramp inherits the road's border color.
- lineWidth: if present, the line width for the bridge or ramp; if absent, the bridge or ramp inherits the road's line width.
- lineBorderWidth: if present, the line border width for the bridge or ramp; if absent, the bridge or ramp inherits the road's border width.
For all the dimensions, percentages are relative to the width of the road.
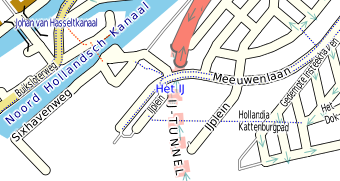
Tunnels can be shown by fading the road, drawing it as a dashed line, or both. Graphics can be drawn to show the mouths of the tunnel.
The tunnel named IJ-TUNNEL above shows all three of these methods and is drawn using this style:
<tunnel dashArray='1,1' mouth='dimgrey' mouthWidth='20%,1' mouthPath='m 0 512 a 512 512 0 1 1 0 -1024'/>
You use the <tunnel> tag inside a <layer> tag (or inside a <condition> in a layer). The <tunnel> attributes are:
- fade: a value in the range 0...1: the amount by which the tunnel is faded compared to a surface-level road. 0 is no fading; 1 makes the tunnel disappear.
- fill: the fill color. If this is not specified, the road's ordinary fill color is used.
- border: the border color. If this is not specified, the road's ordinary border color is used.
- dashArray: the dash array if any. If this is not specified the dash array is inherited from the ordinary road style.
- maxScale: maximum scale (denominator) at which the tunnel style is used
- mouthWidth: width of the tunnel mouth symbol; if a percentage is used it is relative to the width of the road. If SVG is used (see below) the width is used as the width and height of the SVG image.
- mouthPaint: paint used for the tunnel mouth symbol
- mouthPath: a path, using SVG path syntax, for graphics drawn at tunnel mouths. It specifies the right hand end, relative to the end of the tunnel. The other end is generated by reflection. The path units are 1024ths of the line width unless modified by unitsPerLineWidth.
- unitsPerLineWidth: the size of the units in endPath, defined as the number of units equal to the line width. The default value is 1024
Using SVG for tunnel graphics
You can use SVG for more complex graphics for tunnel mouths. Do this by embedding an <svg> element inside a <tunne>l element. For example:
<tunnel dashArray='1,1' fill='yellow' mouthWidth='150%' maxScale='25000'> <svg x='-750' y='-750' width='1500' height='1500'> <linearGradient id="tunnel_gradient" gradientUnits="userSpaceOnUse" x1="0" y1="0" x2="-512" y2="0"> <stop offset="0" style="stop-color:cornflowerblue"/> <stop offset="1" style="stop-color:yellow"/> </linearGradient> <path stroke='none' fill="url(#tunnel_gradient)" d='m 0 -500 a 500 500 0 1 0 0 1000 z'/> <path stroke='brown' fill='none' stroke-width='60' d='m 0 -500 a 500 500 0 1 0 0 1000'/> </svg> </tunnel>
which gives this:
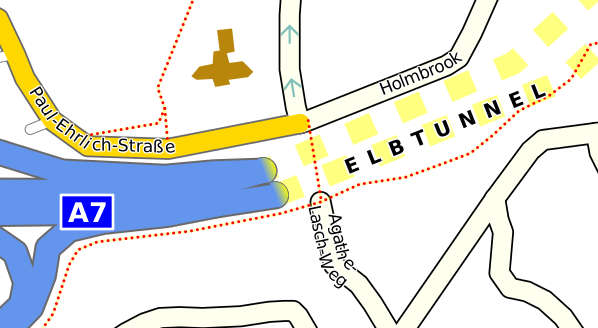
In this example the SVG view rectangle is 1500 units wide, centered on (0,0). The rectangle has to be big enough for the graphics to be rotated to any angle without being clipped off. The width of the SVG rectangle is scaled to the width given by mouthWidth, so 1500 units are scaled to 150% of the line width - therefore 1000 SVG units correspond to the width of the line. The graphics are drawn relative to the right hand end of the tunnel, with (0,0) at the end itself, and the x axis aligned to the direction of the tunnel.
You can use the <oneWayArrow> element to define an arrow symbol to be drawn to show the direction of one-way streets. The <oneWayArrow> attributes are:
- fill: the color used to draw the arrow.
- border: if specified, a border is drawn in this color.
- borderWidth: the width of the border in user units: by default, 1024 units are equal to the width of the road, but you can set the unit size to whatever you like using the unitsPerLineWidth attribute (see below).
- color: if specified, a color to be used to colorize any SVG icon used as the arrow.
- gap: the gap between the left edges of successive symbols, in user units, where 1024 units equal the width of the road (unless modified by unitsPerLineWidth); default value = 1024.
- id: if SVG is used to define the graphics (see below), the identifying name of the icon.
- isLabel: allowed values are 'yes' and 'no'; the default is 'no'. If the value is 'yes', this attribute treats arrows as labels, which means that they are drawn just after the object's label and will not overlap other labels in the same label layer, or other arrows with the 'isLabel' attribute.
- maxScale: the maximum scale factor at which the symbols are drawn. The default is 10000.
- opacity: the opacity used for the fill color.
- path: a path, defined using SVG path data syntax (the 'd' attribute in the element), defining the arrow or other symbol, in a coordinate system where the direction of the road is from left to right and the width of the road is 1024 units, unless modified by unitsPerLineWidth.
- ref: the name of an arrow icon to be drawn; the icon must have been defined in a <defs> element earlier in the style sheet.
- unitsPerLineWidth: the number of units in the path definition that are equal to the width of the road. The default value is 1024.
- width: if SVG is used to define the graphics (see below), the width of the graphics. The default value is the width of the road, and percentages also refer to the width of the road.
- height: if SVG is used to define the graphics (see below), the height of the graphics. The default value is the width of the road, or (if the width attribute was used) the same value as the width. Percentages refer to the width of the road.
Example: a broad transparent yellow arrow:
<oneWayArrow path="M 0 50 H 300 L 40 300 H 180 L 505 0 L 180 -300 H 40 L 300 -50 H 0 Z" fill="yellow" opacity="0.5"/>
If you use <oneWayArrow> on a layer other than "road" it is treated as meaning <repeatedSymbol> and the symbols are unconditionally drawn along the path in the direction in which it is defined.
Using SVG for arrows
For more complex arrow graphics, where a filled shape with an optional border is not enough, use SVG, You can do it like this:
<oneWayArrow gap='2500' opacity='1' isLabel='yes'> <svg x='-500' y='-500' width='1000' height='1000'> <linearGradient id="XXX" gradientUnits="userSpaceOnUse" x1="-500" y1="0" x2="1000" y2="0"> <stop offset="0" stop-color='pink'/> <stop offset="1" stop-color='red'/> </linearGradient> <path fill='url(#XXX)' d='M -450 -50 V 50 H 250 L -100 400 H 50 L 450 0 L 50 -400 H -100 L 250 -50 H -450 Z' /> </svg> </oneWayArrow>
which produces arrows that fade from red to pink along their length.
You can also define the arrow icon in the <defs> section and reference it using the ref attribute.
Repeated symbols and start and end symbols on lines
You can draw repeated symbols along any linear feature. For example, national frontiers are sometimes emphasized using small crosses, and cross-ties can be drawn along railway lines. The attributes you can use are exactly the same as for the oneWayArrow element, except that you use repeatedSymbol instead of oneWayArrow. You cannot use both oneWayArrow and repeatedSymbol for a road.
This feature can be used to place arrows along route lines overlaid on the map by means of of an auxiliary map database.
Using SVG for repeated symbols
You can use SVG to define repeated symbols in exactly the same way as for one-way arrows.
Start and end symbols
Symbols can also be specified for the starts and ends of lines. The startSymbol and endSymbol elements work in the same way as oneWayArrow and repeatedSymbol and allow you to create graphics that is drawn at the start or end of a line only. This can be used for arrow-heads, transverse ticks, and the like.
Dashed, truncated and extended lines
Dashed lines are specified using a syntax similar to that of SVG. Use the attribute dashArray in the <line> or <shape> tag. The value is a comma-separated list of dash and gap sizes, relative to the line width (e.g., the value 2 means a dash or gap twice as long as the line width).
The railway line below is drawn as a dashed line with a border, using this code in the style sheet:
<layer name='railway'> <line width='12m,2pt' border='grey' borderWidth='10%,0.7,2' fill='white' dashArray='5,5'/> <label font-size='75%,8pt' glow='white' color='black' case='assume-title'/> </layer>
White dashes are drawn over a grey border; when there are dashes, the border is also the colour between the dashes.
Truncating and extending lines
Sometimes lines need to be truncated at the start or end or both. For example, a line indicating an airway may need to be shortened so that it doesn't interfere with symbols for navigation aids or position fixes. You can use the truncationAtStart and truncationAtEnd attributes inside <line> or <highlight> elements to shorten lines. All the normal map-related or display-related dimensions can be used, and you can also use percentages, which refer to the width of the line.
Negative values have the effect of extending lines. This can be used to join disconnected sections of highlights drawn along lines (for example, to show traffic density on roads).
Map objects in a single layer often have different attributes. For instance, roads are distinguished by their feature type and by other attributes indicating whether a road is one-way, private, etc. These attributes affect the way the road is drawn.
You use <condition> sections inside <layer> to treat objects with differing attributes in different ways. Each <condition> section is like an embedded <layer> section for only those objects with the specified attributes.
A <condition> section inherits all attributes defined in the containing <layer>, unless it is nested inside another condition, in which case it inherits from the containing condition. Conditions may be nested up to 15 levels deep.
You set the actual condition using a style sheet expression in the exp attribute. Expressions test integer and string attributes of map objects; if the expression is true, the object is drawn using the styles given inside the condition element
This is hard to understand without an example. Here is the mid-level road layer from the standard style sheet:
<layer name='road/mid' road='true'>
<condition exp='@feature_type="tertiary road"'>
<line border='dimgrey' borderWidth='8%,0.35pt,1pt' fill='orange+khaki+0.8white' width='10m@6000_40m@40000,0.3pt'/>
<macro ref='minor-road-label'/>
<macro color='darkkhaki' ref='one-way-arrow'/>
<macro ref='standard-bridge'/>
<macro ref='grey-tunnel'/>
</condition>
<condition exp='@feature_type in { "secondary road", "secondary road link" }'>
<line border='dimgrey' borderWidth='8%,0.35pt,1pt' fill='orange+khaki+0.6white' width='10m@6000_40m@40000,0.6pt'/>
<scale max='40000'>
<label case='assume-title' color='dimgrey' font-size='75%,5pt,18pt' glow='white' glowWidth='7%,0.5pt' labelFormat=';int_name;name:en+" "ref' maxScale='75000'/>
</scale>
<macro color='darkkhaki+black' ref='one-way-arrow'/>
<macro ref='standard-bridge'/>
<macro ref='standard-tunnel'/>
</condition>
</layer>
The first condition has the test '@feature_type="tertiary road"', meaning that only tertiary roads are drawn by the specifications in this condition.
Here is an example showing the inheritance of attributes from the containing layer:
<layer name='waterway/minor'> <label case='assume-title' color='ncsblue' duplicate='1000m,512pt' font-family='serif' font-style='italic' glow='white' glowWidth='7%,0.5pt' position='centralpath' priority='1'/> <line fill='lightblue'/> <shape fill='lightblue'/> <condition exp='@feature_type="str"'> <line width='4m,0.3pt'/> <label font-size='75%,5pt,18pt'/> </condition> <condition exp='@feature_type="dra"'> <line width='2m,0.3pt'/> <label font-size='75%,5pt,18pt'/> </condition> <macro ref='water-minor'/> </layer>
And here is an example of nested conditions:
<layer name='pushpin'> <label case='assume-title' color='ncsred' colorAttrib='_color' font-size='12m,6pt,12pt' glow='white' glowWidth='7%,0.5pt' priority='-20' wrapWidth='5em'/> <condition exp='@=0'> <condition exp='_iconText'> <icon textAttrib='_iconText' font-size='24m,12pt,72pt' color='ncsred' colorAttrib='_color' canOverlap='true'/> </condition> <condition exp='!_iconText'> <icon ref='pushpin-icon' color='ncsred' colorAttrib='_color' canOverlap='yes' canCombine='yes'/> <condition exp='_combined gt 1'> <icon ref='large-pushpin-icon' color='ncsred'/> <label position='icon' labelFormat='_combined' color='ncsred' colorAttrib='_color' font-size='12m,6pt,12pt' glow='white' glowWidth='7%,1' priority='-21' wrapWidth='5em'/> </condition> </condition> </condition> <condition exp='@!=0'> <shape border='ncsred' borderWidth='2m,0.6pt' fill='ncsred' opacity='0.5'/> <line fill='ncsred' opacity='0.5' width='5m,0.6pt'/> </condition> </layer>
Here, the outer two conditions distinguish point pushpin objects ('@=0'; @ is the type, and 0 means a point; 1 means a line, 2 a polygon and 3 an array or texture) from others. Within point objects, those with an _iconText attribute are treated differently from those without, and pushpins without _iconText are drawn using a larger icon if they are the result of combining several pushpins.
When the map is drawn, objects are matched to the innermost test that succeeds.
There are 32 route types, which are a subset of the many feature type values. They can all be tested in style sheet expressions. For example, the expression '@feature_type = "primary road' tests whether a map object is a primary road. The route types are:
- motorway
- motorway link
- trunk road
- trunk link
- primary road
- primary link
- secondary road
- secondary link
- tertiary toad
- unclassified road
- residential road
- track
- service road
- pedestrian road
- vehicular ferry
- passenger ferry
- living street
- cycleway
- path
- footway
- bridleway
- steps
- other road
- unpaved road
- railway
- light rail
- subway
- aerialway
- ski downhill
- ski nordic
- waterway
- unknown route
Every map object has a Feature Type, which is part of its Feature Info value, which is encoded as a 32-bit integer.
You don't have to work with actual numeric values. In style sheet expressions you can test the name, or (if the feature type is not a route type) the three-letter code. The following expressions mean the same:
'@feature_type = "uni"'
'@feature_type = "university"'
The feature types consist of the 32 route types 0...31, and other types, which are created from three-letter codes aaa ... zzz by encoding each letter in five bits, using the values 1...26 for the letters a...z. Here is a C++ function to create a feature code from three lower-case letters:
inline uint32_t constexpr FeatureTypeCode(int A,int B,int C)
{
return (char(A - 'a' + 1) << 10) | (char(B - 'a' + 1) << 5) | (char(C - 'a' + 1));
}
Here are the feature types that are currently defined and which may be used in expressions in makemap rules (.makemap files), and in style sheet conditions:
Motorway = 0,
MotorwayLink = 1,
TrunkRoad = 2,
TrunkLink = 3,
PrimaryRoad = 4,
PrimaryLink = 5,
SecondaryRoad = 6,
SecondaryLink = 7,
TertiaryRoad = 8,
UnclassifiedRoad = 9,
ResidentialRoad = 10,
Track = 11,
ServiceRoad = 12,
PedestrianRoad = 13,
VehicularFerry = 14,
PassengerFerry = 15,
LivingStreet = 16,
Cycleway = 17,
Path = 18,
Footway = 19,
Bridleway = 20,
Steps = 21,
OtherRoad = 22,
UnpavedRoad = 23,
Railway = 24,
LightRail = 25,
Subway = 26,
AerialWay = 27,
SkiDownhill = 28,
SkiNordic = 29,
Waterway = 30,
UnknownRoute = 31,
UnknownNonRoute = 32,
AdminArea1 = FeatureTypeCode('a','a','a'),
AdminArea2 = FeatureTypeCode('a','a','b'),
AdminArea3 = FeatureTypeCode('a','a','c'),
AdminArea4 = FeatureTypeCode('a','a','d'),
AdminArea5 = FeatureTypeCode('a','a','e'),
AdminArea6 = FeatureTypeCode('a','a','f'),
AdminArea7 = FeatureTypeCode('a','a','g'),
AdminArea8 = FeatureTypeCode('a','a','h'),
AdminArea9 = FeatureTypeCode('a','a','i'),
AdminArea10 = FeatureTypeCode('a','a','j'),
Address = FeatureTypeCode('a','d','d'),
Aerodrome = FeatureTypeCode('a','e','r'),
Airport = FeatureTypeCode('a','i','r'),
AirportGate = FeatureTypeCode('a','g','t'),
AirportHoldingPosition = FeatureTypeCode('a','h','p'),
Allotments = FeatureTypeCode('a','l','l'),
AlpineHut = FeatureTypeCode('a','l','p'),
AmbulanceStation = FeatureTypeCode('a','m','b'),
Apron = FeatureTypeCode('a','p','r'),
AerialWayPylon = FeatureTypeCode('a','p','y'),
Artwork = FeatureTypeCode('a','r','t'),
AerialWayStation = FeatureTypeCode('a','s','t'),
AirTerminal = FeatureTypeCode('a','t','e'),
Atm = FeatureTypeCode('a','t','m'),
Attraction = FeatureTypeCode('a','t','t'),
Bar = FeatureTypeCode('b','a','r'),
Basin = FeatureTypeCode('b','a','s'),
Bay = FeatureTypeCode('b','a','y'),
Beach = FeatureTypeCode('b','e','a'),
Beacon = FeatureTypeCode('b','e','c'),
BedAndBreakfast = FeatureTypeCode('b','e','d'),
Bench = FeatureTypeCode('b','e','n'),
Bank = FeatureTypeCode('b','n','k'),
Boatyard = FeatureTypeCode('b','o','a'),
Borough = FeatureTypeCode('b','o','r'),
Boundary = FeatureTypeCode('b','o','u'),
BicycleParking = FeatureTypeCode('b','p','k'),
BicycleRental = FeatureTypeCode('b','r','e'),
BareRock = FeatureTypeCode('b','r','c'),
Barracks = FeatureTypeCode('b','r','k'),
BrownField = FeatureTypeCode('b','r','o'),
BusStop = FeatureTypeCode('b','s','p'),
BusStation = FeatureTypeCode('b','s','t'),
BufferStop = FeatureTypeCode('b','u','f'),
Building = FeatureTypeCode('b','u','i'),
Bunker = FeatureTypeCode('b','u','n'),
Cabin = FeatureTypeCode('c','a','b'),
Cafe = FeatureTypeCode('c','a','f'),
CampSite = FeatureTypeCode('c','a','m'),
Canal = FeatureTypeCode('c','a','n'),
CaveEntrance = FeatureTypeCode('c','a','v'),
CableCar = FeatureTypeCode('c','c','r'),
CableDistributionCabinet = FeatureTypeCode('c','d','c'),
Cemetery = FeatureTypeCode('c','e','m'),
ChairLift = FeatureTypeCode('c','h','a'),
CheckPoint = FeatureTypeCode('c','h','e'),
Chalet = FeatureTypeCode('c','h','l'),
CivilBoundary = FeatureTypeCode('c','i','b'),
Cinema = FeatureTypeCode('c','i','n'),
City = FeatureTypeCode('c','i','t'),
Cliff = FeatureTypeCode('c','l','f'),
Clinic = FeatureTypeCode('c','l','i'),
Commercial = FeatureTypeCode('c','m','r'),
Coastline = FeatureTypeCode('c','o','a'),
College = FeatureTypeCode('c','o','l'),
Common = FeatureTypeCode('c','o','m'),
Construction = FeatureTypeCode('c','n','s'),
Conservation = FeatureTypeCode('c','n','v'),
Continent = FeatureTypeCode('c','o','n'),
County = FeatureTypeCode('c','o','u'),
CarPark = FeatureTypeCode('c','p','k'),
CarRental = FeatureTypeCode('c','r','e'),
Crossing = FeatureTypeCode('c','r','o'),
Country = FeatureTypeCode('c','r','y'),
CarSharing = FeatureTypeCode('c','s','h'),
CutLine = FeatureTypeCode('c','u','t'),
CarWash = FeatureTypeCode('c','w','a'),
CaravanSite = FeatureTypeCode('c','v','n'),
CyclingRoute = FeatureTypeCode('c','y','r'),
Dam = FeatureTypeCode('d','a','m'),
DangerArea = FeatureTypeCode('d','a','n'),
Dentist = FeatureTypeCode('d','e','n'),
Disused = FeatureTypeCode('d','i','s'),
Ditch = FeatureTypeCode('d','i','t'),
Dock = FeatureTypeCode('d','o','c'),
DogPark = FeatureTypeCode('d','o','g'),
Drain = FeatureTypeCode('d','r','a'),
DragLift = FeatureTypeCode('d','r','g'),
Doctors = FeatureTypeCode('d','r','s'),
District = FeatureTypeCode('d','s','t'),
ElectricVehicleCharging = FeatureTypeCode('e','v','c'),
Farm = FeatureTypeCode('f','a','r'),
FarmYard = FeatureTypeCode('f','a','y'),
Fell = FeatureTypeCode('f','e','l'),
FerryTerminal = FeatureTypeCode('f','e','t'),
FastFood = FeatureTypeCode('f','f','d'),
FireExtinguisher = FeatureTypeCode('f','i','e'),
FireFlapper = FeatureTypeCode('f','i','f'),
FireHose = FeatureTypeCode('f','i','h'),
FireStation = FeatureTypeCode('f','i','s'),
FitnessStation = FeatureTypeCode('f','i','t'),
FireHydrant = FeatureTypeCode('f','i','y'),
Forestry = FeatureTypeCode('f','o','r'),
Fishing = FeatureTypeCode('f','s','h'),
Fuel = FeatureTypeCode('f','u','e'),
Funicular = FeatureTypeCode('f','u','n'),
Garages = FeatureTypeCode('g','a','r'),
Gate = FeatureTypeCode('g','a','t'),
Garden = FeatureTypeCode('g','d','n'),
Generator = FeatureTypeCode('g','e','n'),
GreenHouse = FeatureTypeCode('g','h','o'),
Glacier = FeatureTypeCode('g','l','a'),
GolfCourse = FeatureTypeCode('g','o','l'),
Gondola = FeatureTypeCode('g','o','n'),
GoodsAerialWay = FeatureTypeCode('g','o','o'),
Grass = FeatureTypeCode('g','r','a'),
GreenField = FeatureTypeCode('g','r','e'),
GritBin = FeatureTypeCode('g','r','b'),
GraveYard = FeatureTypeCode('g','r','y'),
GuestHouse = FeatureTypeCode('g','u','e'),
Halt = FeatureTypeCode('h','a','l'),
Hamlet = FeatureTypeCode('h','a','m'),
Hangar = FeatureTypeCode('h','a','n'),
Heath = FeatureTypeCode('h','e','a'),
Helipad = FeatureTypeCode('h','e','l'),
RailwayHalt = FeatureTypeCode('h','l','t'),
HikingRoute = FeatureTypeCode('h','i','k'),
HorseRiding = FeatureTypeCode('h','o','r'),
Hospital = FeatureTypeCode('h','o','s'),
Hotel = FeatureTypeCode('h','o','t'),
HorseRidingRoute = FeatureTypeCode('h','r','r'),
Hostel = FeatureTypeCode('h','s','t'),
IceRink = FeatureTypeCode('i','c','e'),
Industrial = FeatureTypeCode('i','n','d'),
Information = FeatureTypeCode('i','n','f'),
Island = FeatureTypeCode('i','s','l'),
IsolatedDwelling = FeatureTypeCode('i','s','o'),
Junction = FeatureTypeCode('j','c','t'),
Kindergarten = FeatureTypeCode('k','i','n'),
LandFill = FeatureTypeCode('l','a','n'),
Land = FeatureTypeCode('l','n','d'),
LevelCrossing = FeatureTypeCode('l','e','v'),
Library = FeatureTypeCode('l','i','b'),
Locality = FeatureTypeCode('l','o','c'),
LockGate = FeatureTypeCode('l','o','k'),
MaritimeBoundary = FeatureTypeCode('m','a','b'),
Mall = FeatureTypeCode('m','a','l'),
Marsh = FeatureTypeCode('m','a','r'),
Meadow = FeatureTypeCode('m','e','a'),
Military = FeatureTypeCode('m','i','l'),
Marina = FeatureTypeCode('m','n','a'),
Motel = FeatureTypeCode('m','o','t'),
MinorPowerLine = FeatureTypeCode('m','p','l'),
MiniatureGolf = FeatureTypeCode('m','r','g'),
MiniatureRailway = FeatureTypeCode('m','r','y'),
Mud = FeatureTypeCode('m','u','d'),
Municipality = FeatureTypeCode('m','u','n'),
Museum = FeatureTypeCode('m','u','s'),
NatureReserve = FeatureTypeCode('n','a','t'),
NationalPark = FeatureTypeCode('n','a','p'),
NavalBase = FeatureTypeCode('n','a','v'),
Neighborhood = FeatureTypeCode('n','e','i'),
NursingHome = FeatureTypeCode('n','u','r'),
Orchard = FeatureTypeCode('o','r','c'),
PrecisionApproachPathIndicator = FeatureTypeCode('p','a','p'),
Park = FeatureTypeCode('p','a','r'),
PublicBuilding = FeatureTypeCode('p','b','u'),
PostBox = FeatureTypeCode('p','b','x'),
PostCode = FeatureTypeCode('p','c','o'),
PicnicTable = FeatureTypeCode('p','c','t'),
Peak = FeatureTypeCode('p','e','a'),
Pharmacy = FeatureTypeCode('p','h','a'),
Phone = FeatureTypeCode('p','h','o'),
PicnicSite = FeatureTypeCode('p','i','c'),
Pier = FeatureTypeCode('p','i','e'),
Pipeline = FeatureTypeCode('p','i','p'),
ParkingEntrance = FeatureTypeCode('p','k','e'),
Parking = FeatureTypeCode('p','k','g'),
ParkingSpace = FeatureTypeCode('p','k','s'),
PlantNursery = FeatureTypeCode('p','l','a'),
Platform = FeatureTypeCode('p','l','f'),
PlaceOfWorship = FeatureTypeCode('p','l','w'),
Playground = FeatureTypeCode('p','l','y'),
PostOffice = FeatureTypeCode('p','o','f'),
Police = FeatureTypeCode('p','o','l'),
Position = FeatureTypeCode('p','o','s'),
ProtectedArea = FeatureTypeCode('p','r','a'),
PowerSubStation = FeatureTypeCode('p','s','s'),
Pub = FeatureTypeCode('p','u','b'),
PowerLine = FeatureTypeCode('p','w','l'),
PowerStation = FeatureTypeCode('p','w','s'),
Quarry = FeatureTypeCode('q','a','r'),
Quarter = FeatureTypeCode('q','r','t'),
Range = FeatureTypeCode('r','a','n'),
Rapids = FeatureTypeCode('r','a','p'),
Recycling = FeatureTypeCode('r','c','y'),
RecreationGround = FeatureTypeCode('r','e','c'),
Reef = FeatureTypeCode('r','e','e'),
Region = FeatureTypeCode('r','e','g'),
Retail = FeatureTypeCode('r','e','t'),
Ridge = FeatureTypeCode('r','i','j'),
River = FeatureTypeCode('r','i','v'),
Rock = FeatureTypeCode('r','o','c'),
RoundHouse = FeatureTypeCode('r','o','u'),
ResidentialArea = FeatureTypeCode('r','s','d'),
Restaurant = FeatureTypeCode('r','s','t'),
Reservoir = FeatureTypeCode('r','s','v'),
Runway = FeatureTypeCode('r','u','n'),
Route = FeatureTypeCode('r','u','t'),
RiverBank = FeatureTypeCode('r','v','b'),
SaltPond = FeatureTypeCode('s','a','l'),
Sand = FeatureTypeCode('s','a','n'),
Sauna = FeatureTypeCode('s','a','u'),
School = FeatureTypeCode('s','c','h'),
Scree = FeatureTypeCode('s','c','r'),
Scrub = FeatureTypeCode('s','c','b'),
Sea = FeatureTypeCode('s','e','a'),
StateEmergencyServiceStation = FeatureTypeCode('s','e','s'),
Shop = FeatureTypeCode('s','h','o'),
SkiRoute = FeatureTypeCode('s','k','r'),
Slipway = FeatureTypeCode('s','l','i'),
SportsCenter = FeatureTypeCode('s','p','o'),
SportsPitch = FeatureTypeCode('s','p','p'),
Spring = FeatureTypeCode('s','p','r'),
SportsTrack = FeatureTypeCode('s','p','t'),
State = FeatureTypeCode('s','t','a'),
Stadium = FeatureTypeCode('s','t','m'),
RailwayStation = FeatureTypeCode('s','t','n'),
Station = FeatureTypeCode('s','t','n'), // deliberate duplicate
Stone = FeatureTypeCode('s','t','o'),
StopPosition = FeatureTypeCode('s','t','p'),
Stream = FeatureTypeCode('s','t','r'),
Strait = FeatureTypeCode('s','t','t'),
Suburb = FeatureTypeCode('s','u','b'),
Supermarket = FeatureTypeCode('s','u','p'),
SurveyPoint = FeatureTypeCode('s','u','r'),
SubwayEntrance = FeatureTypeCode('s','w','e'),
SwimmingPool = FeatureTypeCode('s','w','i'),
Tank = FeatureTypeCode('t','a','n'),
Taxi = FeatureTypeCode('t','a','x'),
Theatre = FeatureTypeCode('t','h','e'),
ThemePark = FeatureTypeCode('t','h','p'),
Toilet = FeatureTypeCode('t','o','i'),
Town = FeatureTypeCode('t','o','w'),
TurningCircle = FeatureTypeCode('t','c','i'),
TurningPoint = FeatureTypeCode('t','p','t'),
Tram = FeatureTypeCode('t','r','a'),
Tree = FeatureTypeCode('t','r','e'),
TrafficSignals = FeatureTypeCode('t','r','f'),
TrackPoint = FeatureTypeCode('t','r','p'),
TreeRow = FeatureTypeCode('t','r','r'),
TramStop = FeatureTypeCode('t','r','s'),
TurnTable = FeatureTypeCode('t','u','r'),
Tower = FeatureTypeCode('t','w','r'),
Taxiway = FeatureTypeCode('t','w','y'),
University = FeatureTypeCode('u','n','i'),
VisualApproachSlopeIndicator = FeatureTypeCode('v','a','s'),
VillageGreen = FeatureTypeCode('v','i','g'),
Village = FeatureTypeCode('v','i','l'),
Vineyard = FeatureTypeCode('v','i','n'),
ViewPoint = FeatureTypeCode('v','i','w'),
Volcano = FeatureTypeCode('v','o','l'),
Waterfall = FeatureTypeCode('w','a','f'),
WaterPark = FeatureTypeCode('w','a','p'),
Water = FeatureTypeCode('w','a','t'),
Weir = FeatureTypeCode('w','e','r'),
Wetland = FeatureTypeCode('w','e','t'),
Windsock = FeatureTypeCode('w','i','s'),
WalkingRoute = FeatureTypeCode('w','l','k'),
Wood = FeatureTypeCode('w','o','o'),
Works = FeatureTypeCode('w','o','r'),
Waypoint = FeatureTypeCode('w','p','t'),
WaterTower = FeatureTypeCode('w','t','t'),
WaterWell = FeatureTypeCode('w','t','w'),
Zoo = FeatureTypeCode('z','o','o'),
// legacy types for backward compatibility
LegacyBridleway = FeatureTypeCode('b','r','i'),
LegacyCycleway = FeatureTypeCode('c','y','c'),
LegacyFootway = FeatureTypeCode('f','o','o'),
LegacyLightRail = FeatureTypeCode('l','i','r'),
LegacyMonorail = FeatureTypeCode('m','o','n'),
LegacyNarrowGauge = FeatureTypeCode('n','a','r'),
LegacyPreservedRailway = FeatureTypeCode('p','r','y'),
LegacyRailway = FeatureTypeCode('r','l','y'),
LegacySteps = FeatureTypeCode('s','t','e'),
LegacySubway = FeatureTypeCode('s','w','y'),
LegacyTram = FeatureTypeCode('t','r','a'),
Invalid = INT16_MAX
This release, 9.2, was made on 8th October 2025 and was based on commit 9.2-0-g8cef7d2df.
The previous release, 9.0, was made on 2nd June 2025 and was based on commit 9.0-0-g6f54cbf72.
The main change is the introduction of a new configurable file loading system using file policies, which saves significant runtime RAM.
This release, 9.0, was made on 2nd June 2025 and was based on commit 9.0-0-g6f54cbf72.
The previous release, 8.12, was made on 7th November 2024 and was based on commit 8.12-19-g3f49c29ef.
The main changes are the introduction of an auto-map-loader, allowing sets of tiles, possibly overlapping, to be loaded and unloaded automatically to cover a larger map, and the simplification of the router state, meaning that only one current route can exist at a time.
This release, 8.12, was made on 7th November 2024 and was based on commit 8.12-19-g3f49c29ef.
The previous release, 8.10, was made on 28th May 2024 and was based on commit 8.9-312-g25b22d38f.
The most important changes are that support for voice instructions during navigation has been added; and most identifiers in the iOS API have been renamed, for reasons explained below.
This release was made on 28th May 2024 and is based on commit 8.9-312-g25b22d38f in the Git repository.
The previous release, 8.8, was made on 1st February 2024 and was based on commit 8.7-304-gf1fb8f68d in the Git repository.
The main change is the addition of support for online Mapbox vector tile data for display, searching and geocoding.
This release, 8.8, was made on 1st February 2024 and is based on commit 8.7-304-gf1fb8f68d in the Git repository. There are no source incompatibilities with 8.6. The main change is that re-routing is now done by a background thread during navigation, allowing applications to remain responsive.
The previous release, 8.6, was made on 8th August 2023 and was based on commit 8.6-1-gc0939f76f in the Git repository.
The main change is the introduction of background route calculation.
Release date: 26th June 2015
Previous release: 3.3, 13th May 2015
Release date: 9th September 2015
Previous release: 3.4, 26th June 2015
CartoType release 4.0
and how it differs from release 3
Changes affecting all APIs
The Legend API
The new Legend API allows you to create consistent, good-looking and flexible legends (scale bars and keys to symbols) as separate images which can be overlaid on the map or drawn elsewhere.
Consistent argument order for the Find functions
The many Find functions now order their arguments consistently. The destination array always comes first, followed by the maximum object count if applicable, and so on. These changes also affect the non-C++ APIs.
C++
Moving to C++11
The main theme of the changes is a move to modern C++. C++11 is supported on all major platforms, including Windows (VS2015), iOS (Xcode), the Android NDK (gcc), and Linux (gcc).
Memory allocation failure throws an exception
CartoType's builds formerly disabled exceptions and handled out-of-memory conditions by using a memory allocator which returned null when out of memory. The error KErrorNoMemory was then propagated back up the stack. CartoType 4.0 uses exceptions, and throws std::bad_alloc when an allocation fails. Other errors like failing to open a file are still handled using error codes.
Arrays are std::vector objects
CartoType's main two array classes are now publicly derived from std::vector:
template<class T> class CArray: public std::vector<T>
template<class T> class CPointerArray: public std::vector<T*>
That means you can now use all the std::vector functions and algorithms. Of course, because memory allocation failure now throws an exception, array functions no longer return error codes.
Sample code showing the use of range for with a CartoType array:
CPointerArray<CBaseMapObject> found_objects;
my_framework->Find(found_objects,find_param);
for (const auto p : found_objects)
{
size_t everywhere
Many argument and return types have changed from int32 to size_t to avoid warnings when using the new array classes based on std::vector.
CString
CartoType::CString now has value semantics, which means you can assign strings to each other, pass them as function arguments, return them from functions, and create arrays of them. A CString still holds UTF-16 text, but can now be constructed from null-terminated 8-bit strings, and also from std::string. You can even construct a string from nullptr, which makes it easy to have default CString arguments: void myfunc(CString aText = nullptr). All this means that…
String arguments are simpler
Most functions taking string arguments now take CString or const CString&. Overloads taking const char* no longer exist. But thanks to the new CString constructors you can pass 8-bit string literals or std::string objects if you like.
So you can call CFramework::LoadMap in these different ways:
my_framework->LoadMap("england.ctm1");
std::string map_name1("wales.ctm1");
my_framework->LoadMap(map_name1);
CString map_name2("scotland.ctm1");
my_framework->LoadMap(map_name2);
Observer interface: MFrameworkObserver
The new observer interface allows you to provide an observer object to a CartoType::CFramework object. The observer receives notifications of changes to the framework state. It is intended for the use of higher-level GUI objects which need to update their display after framework state has been changed programmatically. For example, if a route is created, dynamic map objects need to be redrawn.
British national grid functions
There are some new functions to convert back and forth between British national grid references and other position formats. They are useful when comparing CartoType maps of Great Britain with Ordnance Survey maps.
CT_IMPORT and CT_EXPORT have gone
The macros CT_IMPORT and CT_EXPORT were used in older versions of CartoType to declare functions as exported from DLLs. The C++ SDK is no longer built or shipped as a DLL, therefore these macros have been abolished.
Simpler functions to set and get string attributes
The functions to set and get string attributes have been simplified. For example, where you formerly wrote:
CString key; key.Set("addr:street");
TText street;
my_map_object->GetStringAttribute(&key,street);
you can now write
CString street = my_map_object->GetStringAttribute("addr:street");
The makemap tool
No more support for old-style import scripts
Two obsolete import script formats are no longer supported. They are the old OSM rule format with the extension .osm_to_ctm1_rules, and the old shapefile rule format with the extension xml. The new .makemap format replaces them both.
In particular, when you import coastlines from shapefile data you should use a coastlines.makemap file with this content (adjusting the filename as necessary):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<CartoTypeImportRules>
<file name='\coastlines-complete\land_polygons.shp'>
<commit layer='outline'/>
</file>
</CartoTypeImportRules>
The .makemap import rules format is described here: http://www.cartotype.com/import-rules-used-by-makemap.html .
Changes affecting all APIs
Gradients can be used in routing
You can add gradients to route data using the makemap command-line options /route=ag (A-star routing with gradients) or /route=cg (contraction hierarchy routing with gradients). For this to work you have to load the elevation data from USGS .hgt files using the /usgs option. For more details about the /usgs option see the main article about creating maps.
If you add gradients, one of eight gradients (flat or slight, gentle, steep and very steep, each in an uphill or downhill varient) is stored for every route segment. You can add speed weightings and bonuses to the route profile for the gradients, and specify which road types the gradient weightings apply to.
Loading and saving routes
Route objects now contain the route profile used to create them, which means you no longer have to specify a profile when saving a route. You can now load or save routes in files or strings, and you can load routes from GPX files, in which case the GPX track is converted to a legal route. All route loading and saving functions allow you to use either .ctroute or GPX format.
Layer names
You can get all the layer names in a single array using a new LayerNames or layerNames function.
Changes to the C++ API
Smart pointers
Functions creating objects (e.g., New functions, LoadMapObject) now return std::unique_ptr, not a raw pointer. This makes it much easier to manage their lifetimes.
String properties
String properties like Name, Locale and Proj4Param that were formerly returned as const char* are now returned as std::string, making it easier to write safe code.
Setting camera parameters in perspective view
The new SetPerspective overload takes a TPerspectiveParam object which allows you to set camera height, angle, rotation, field of view and other parameters.
Framework observers
Framework observers are now supported, primarily for use by CartoType GL.
Multiple framework observers are now supported: AddObserver and RemoveObserver replace SetObserver.
Changes to the Android Java API
Framework observers
Framework observers are now supported, primarily for use by CartoType GL.
Release 4.2 makes relatively few API changes. Its purpose is mainly to merge in a large number of internal changes from the main development branch.
Changes affecting all platforms
ReverseRoutes function
The new ReverseRoutes or reverseRoutes function reverses current routes, replacing them with new routes from the former end to the former start.
Changes to the C++ API
CMapObject
The CBaseMapObject class has been abolished. The public map object class is now CMapObject.
CMapObjectArray
There is a convenience declaration, CMapObjectArray, defined as std::vector<std::unique_ptr<CMapObject>> CMapObjectArray, which is used when returning map objects from Find functions. It replaces all former uses of CPointerArray<CBaseMapObject>. The use of unique pointers clarifies ownership and makes the objects easier to manage.
CBitmap
CBitmap functions which create modified bitmaps now return CBitmap objects, not std::unique_ptr<CBitmap>. There is no loss of performance because move operations are used internally.
Indication of turn-off
The TTurn class now has a member iTurnOff indicating whether is a turn off, defined as a turn on to a lower-status road.
Changes to the .NET API
MapObjectList
There is a new class, MapObjectList, defined as System.Collections.Generic.List<CartoType.MapObject>, which is used when returning map objects from Find functions. It replaces all former uses of List<MapObject>. One advantage of this change is that it allows documentation for Find functions to be shown in the Visual Studio Object Browser. Formerly, the presence of < and > signs in the C++/CLI type List<MapObject^>^ prevented in-source documentation for the Find functions from being created during compilation.
Changes to the Android API
Licensing functions
Two new functions, Framework.license and Framework.licensee, allow you to supply a license key and get the licensee name respectively.
deleteRoutes
The new deleteRoutes function deletes all current routes.
- Release notes for CartoType 4.4
- Release notes for CartoType 4.3
- Release notes for CartoType 5.0
- Release Notes for CartoType 7.0
- Release Notes for CartoType 7.2
- Release Notes for CartoType 7.4
- Release Notes for CartoType 7.6
- Release Notes for CartoType 7.8
- Release Notes for CartoType 8.0
- Release Notes for CartoType 8.2